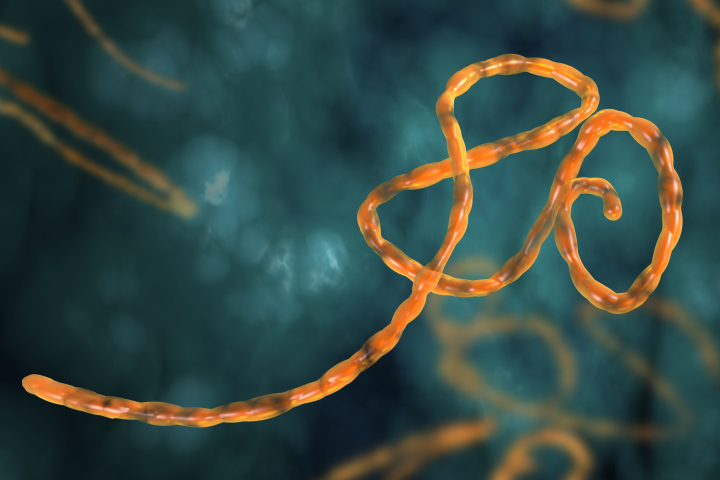
Ebola Virus which caused a fatal blow in African regions put World Health Organization (WHO) in an emergency situation. The number of people who became infected by Ebola Virus is increasing every day, but there is not clear or absolute method of treatment. In certain area, special watch on traveling command has been issued, and airports are processing extra rigorous entry procedure. Some medical teams have been infected to Ebola Virus while giving their best attempt to eradicate Ebola Virus and treat the patients. Let’s learn more about Ebola Virus which has not been dying out easily.
1. What is Ebola Virus?
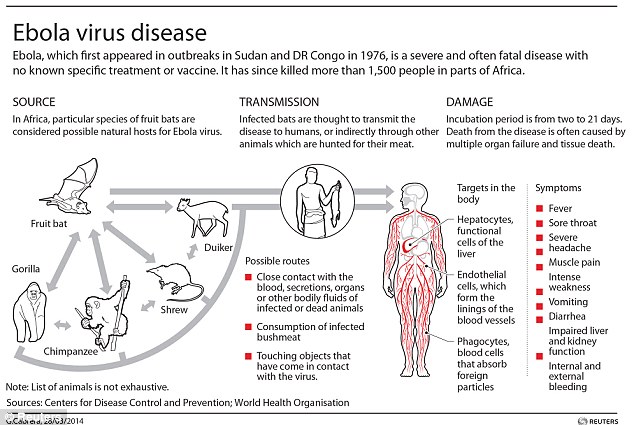
In 1976, Ebola Virus was first discovered in Democratic Republic of the Congo, and it was named ‘Ebola’ after that of the nearby river. The sources of infection or natural hosts are assumed to be fruit bat, gorilla, chimpanzee, porcupine (rodents). In 2014, Ebola Virus began to break out from Western Africa such as Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone, and more than 3,500 were infected, and 1,900 died. The virus can be infected through contact of infected carcass or meat or through infected person’s body fluid such as dead skin cell, wound, mucous membrane, blood, urine, and semen. However, contact through air does not have an impact. In the beginning phase of Ebola infection, symptoms of fever, headache, chill, muscle pain, loss of appetite, vomit, diarrhea, and rash. All of these symptoms are very similar with those of other illnesses such as sore throat, malaria, typhoid. After the infection, rash and bleeding become serious, and it entails organ failures such as failing function of kidney and liver, decline of the number of white blood cell and platelet, decrease of blood volume caused by increase of hepatic enzyme, a mysterious death. It takes 2 to 21 days from incubation period to manifestation of symptoms, and the infected can die around the tenth day of outbreak. The fatality rate is from 25% to up to 90%, and some patients revive after being infected. Even though it has high fatality rate, since its power or propagation is weak that there is low chance of Ebola Virus out breaking throughout the whole world just like the case of H1N1 in 2009.
2. Countries with Danger and the Aftermath
In the past, Ebola Virus usually broke out in the Middle Africa, and only one was infected in Ivory Coast of Western Africa in 1994. However, this Ebola Virus epidemic of 2014 is the biggest one that ever occurred, and the virus has hit Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, and Lagos of Nigeria.

a. The Red Light in Western Africa Countries
The infection of Ebola Virus is occurring with dense concentration only in specific regions such as Western Africa. Looking at the infected or deceased of each country announced by WHO in August 28th, Liberia was most fatally hit with 1,378 infected and 694 deceased. Guinea had next biggest number of death, 430 deceased and 648 infected. Even though Sierra Leone had less number of deaths, it had greater number of infected, 422 deceased and 1,026 infected. In Nigeria, 17 people were infected and 6 people died. This number has been increasing; in September, there has been additional 400 deceased less than a week.
Due to the deepening Ebola Virus crisis, the four countries of Western Africa faced economic downturn. Donald Kaberuka, President of African Development Bank (AfDB) visited Sierra Leone and forecasted, “The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of countries of this region would decreased by minimum 1% up to 4%,” and explained, “The amount is as enormous as six hundred million dollars.” He picked the reasons for the declined GDP as decreased revenue, weakened exchange rate, instability of the market, the halt of flight, and business plan cancellation of investors.
Nigeria has smaller number of infected and deceased compared to other Western Africa countries, but since it has the most population in Africa, the damage of human life can be the greatest any time. Thus, in order to prevent further spread of Ebola Virus, the government of Nigeria is taking a prompt action. To prevent Ebola Virus diffusion of 2nd infection and train school teachers to handle Ebola Virus infection, the school has been closed until October 13th. Nigeria’s capital, Abuja’s public officer, Ali Sadiq, mentioned, “It was a great decision of the government to close the school,” and showed concern, “But the period of school closer too long.”
Ministry of Health confirmed that Senegal had its 1st case of Ebola. An infected student, despite the closed border, traveled by road to Senegal and brought the disease to the country. Since Senegal is a tourist and transport hub, more caution is required since it has high change of farther spread of Ebola.

b. Ebola mutation, Break Out into Middle and Eastern Africa
There has been worry concerning Ebola Virus that it already has affected Middle Africa and there is a chance of it spreading to Eastern Africa. In Zera Village, Boende, North Western Equateur of Congo located in Middle Africa, 13 people including 5 medical team members passed away from Ebola Virus. In response, Congo health care center has isolated patients with Ebola symptoms and the regions, and is tracing 80 people who already had contacted with those who were infected. However, this Ebola Virus seems to be occurred independently rather than infected from Western Africa. Congo Minister of Department of Health explained, “These cases are not related to break out of Ebola Virus in Western Africa, and the virus is a different mutant.”
WHO designated Kenya located in Eastern Africa as the most potential place for outbreak of Ebola Virus. There has not been any broadcast of Ebola infection, but still those regions are not safe from infection because Kenya is the traffic exchange hub which connects Eastern Africa to Western Africa. Nevertheless, Kenya did not yet ban flight from the four infected countries in Western Africa. In order to prevent the spread of Ebola Virus to East, Kenya needs to minimize the performance of human interchange with infected countries and avoid Ebola Virus before it hits the country.
3. Vaccine and Method of Treatment

Since Ebola Virus disease prevails in only certain African countries rather than worldwide, the development of vaccine has been very slow. So far, no special treatment that can eradicate Ebola Virus exists, but shock or decrease of blood volume and conservative treatment for hemorrhagic tendency have been performed. Humanized monoclonal antibody such as ZMapp are used experimentally.
ZMapp that was approved by American Food and Drug Administration (FAD) and WHO on August 12th, uses a tobacco leaf as the ingredient. When one injects Ebola Virus to a mouse, antibody is created in the blood of the mouse. By injecting DNA, extracted from this antibody, into a tobacco seeding and growing the tobacco, protein, needed for antibody production, is created. However, since this antibody is produced through plant extraction, mass production is difficult, and it takes a couple of months to refine the protein and make it into a medicine. Despite the flaw, the effectiveness has been confirmed through chimpanzee experience, and ZMapp has been administered to American medical team patients.
Japan is also developing medicine for Ebola Virus treatment. A medicine originally created for influenza treatment has been injected to a chimpanzee infected by Ebola Virus, and effectiveness was manifested. This medicine has a couple of advantages compared to ZMapp. This medicine has already been confirmed safe for human body, and mass production is possible since it is synthesized by chemical. In an epidemic laboratory of China, Hwa-Da DNA Laboratory, has developed diagnosis reagent that can detect Ebola Virus and requested an emergency evaluation to State Food and Drug Administration. During the past, Hwa-Da DNA Laboratory has discovered and diagnosed various viruses such as SARS virus and highly pathogenic influenza virus (H5N1) and developed diagnosis reagent for H7N9 and AI. Currently it has finished analysis of antibody DNA of Ebola Virus, so there is hope that it wouldn’t take much to develop the vaccine.
In the market, some people even came up with fake medicines with the intention to earn money using the fear of Ebola Virus. Nano Silver, a dietary supplement containing minute particles of silver is being disguised as a real medicine. Even in Nigeria, ‘sacred Ebola treatment salt’ is sold because of the myth that salt water shower can prevent Ebola Virus. According to WHO, two Nigerians passed away after consuming too much salt water. Thus, WHO and FDA warned people of fake Ebola Virus treatment and medicine.
4. Ebola Myth
In the midst of worldwide fear for Ebola Virus, baseless rumors are adding a bigger confusion and chaos. According to the US ABC broadcast, Liberia, Sierra Leone, and Guinea citizens often block the entrance of medical team coming to figure out the number of patients and apply disinfection fumigation. This is the response to a groundless rumor that medical teams spread Ebola Virus and the disinfection fumigation gas cause death to people. There is even an argument that medical teams are searching for organs for illegal transaction with the excuse of Ebola. Some even believe that when visiting a hospital, one would get infected by Ebola on the spot or die of starvation with negligence. The situation has been exacerbated since some people hesitate to go to the hospital even when suspicious symptoms of Ebola can be detected.
The regional government and medical teams have brought this kind of mistrust of the citizens upon themselves. In Liberia, there was a case where two male citizens with Ebola Virus symptoms died in the street, and the corpse were neglected for four days. In addition, sometimes, patients could not receive proper help when they visited the hospital because medical teams had closed the hospital or ran away with the fear of infection. It is unfortunate to see the irresponsible attitude of the medical teams. On the other hand, their actions and fear are somewhat understandable considering more than 240 medical team members have been infected and more than 120 passed away of Ebola Virus.
5. The Prospect of the Future and Measure of Prevention
Thomas Frieden, the director of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) predicted that the outbreak of Ebola virus did not reach its peak yet and can be more exacerbated. He explains, “The actual amount of Ebola infected and perished is much greater because it is difficult to keep on counting since the figure is increasing too rapidly rather than people try to conceal the figure.” In order to deal with Ebola crisis, more active and systematic actions from the international society is required.
Even though various method to prevent the first infection of Ebola Virus has been investigated, it is difficult to cure or stop the spread of Ebola Virus due to lack of information on natural hosts or sources of infection. Thus, as now, the best thing to do is isolating patients infected by Ebola and prevent others from contacting blood or body fluid of the patients preventing additional infection. Medical centers located in areas prevalence of Ebola virus need to acquire the condition to isolate when patients occur and prepare gloves, gowns, glasses, and other equipment to protect the medical teams. In daily life, it is best to avoid traveling infected countries and contacting bats, rodents, and anthropoid apes, and of course infected patients. Basic prevention regulations such as washing hands are recommended, and after coming back from traveling close watch on suspicious symptoms is needed.

