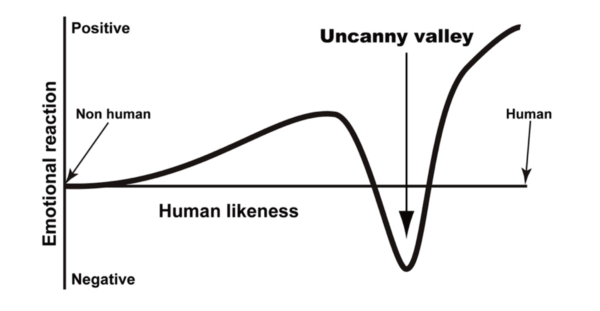
Have you ever heard about ‘uncanny valley’? You may have experienced some unpleasant feelings in response to a humanlike being. Uncanny valley is a theory of emotional response to non-human beings introduced in 1970 by Japanese roboticist Masahiro Mori. It says that an object which imperfectly resembles actual human beings can provoke uncanny feelings. According to this theory, as the degree of an object’s resemblance to a human being increases, the likeability of the observer to the object increases. Then, when the similarity reaches some degree, the likeability falls sharply. When the similarity continues to increase, the likeability rises again rapidly. It was named ‘uncanny valley’ in that there is a deep valley between positive and negative feelings. The theory, which defined the rules for likeability, has become a hot topic as many people experienced ‘uncanny’ feelings in cultural contents. Then, let’s take a look at what uncanny valley is in detail.
Into the Uncanny Valley
Gentle Slope Section
Introducing the uncanny valley, Masahiro Mori plotted it on a graph. The x-axis of the graph is the human likeness of an object and the y-axis is the likeability to such object. The graph has three sections and first one is ‘gentle slope section.’ Here, as the x-axis increases, that is, as the resemblance to a human being increases, the likeability to it also increases. Industrial robots have no resemblance to humans. If an object does not resemble a human being at all like the industrial robots, the likeability to it is close to zero. As the object begins to increasingly resemble humans, the likability increases. The characters of Disney animations are a typical example. Especially, <Frozen II>, which was released in 2019, has received great acclaim for its delicate graphics, and the main characters ‘Elsa’ and ‘Anna’ remain very popular. The reason why the likeability increases in this section is that humans find something in common with the non-human beings and have a positive feeling in the process.


Deep Valley Section: Welcome to Uncanny Valley
When the likeability peaked with increasing similarity, the likeability falls sharply into the deep valley. Humans, who previously found something in common with human-like objects, become to have a negative sentiment about objects that exceeded some degree of similarity. In other words, humans focus on the differences, not the similarities with objects in this section. And these differences trigger a negative feeling. A prime example when describing uncanny valley is the movie <The Polar Express> released in 2004. Many experts said that “it showed the technology to make graphics that look almost exactly like a real human.” But many children who watched the movie responded that they were scared and even some burst into tears. Finally, the movie failed to be a hit at the box office. This is because the unnatural characters in the movie that imperfectly resemble human beings aroused unpleasant feelings in the children.

Steep Slope Section
When the human likeness increases further beyond the uncanny valley, the likeability sharply rises again. According to the graph, objects in this section are almost human-like robots or humans themselves. ‘Free AI Generated Photos’ is popular recently. ‘Icons 8’, a company that makes stock photos provides virtual portrait photos on a sited named ‘Generated Photos.’ All of the photos appear to be of ordinary people, but all of which are actually virtual faces created by artificial intelligence. The site creates and provides their users with characters of various races, facial types and ages. Many people, including graphic designers, are now using the Generated Photo because they have no worries about portrait rights and the photos are free. Unlike the previous uncanny valley, many people showed no displeasure with the AI-generated photos, which look almost exactly like real human beings.

The Reason of the ‘Uncanny’
Then, what is the exact reason why the degree of likeability varies so widely depending on the similarity with humans? This can be seen through the concept of the ‘uncanny.’ Before Masahiro Mori used the term ‘uncanny valley’, a German psychologist, Ernst Anton Jentsch, first set out the concept of the uncanny in 1906. According to Jentsch, each person sets a certain direction and tries to maintain a state based on the direction. But when facing a situation in which they lose their direction, they feel an anxious and unfamiliar feeling. Jentsch defined this feeling as ‘uncanny.’ This, in other words, is a sense of anxiety that comes from an inconsistency. Thalia Wheatley, a professor of psychology at Dartmouth College, said that through our evolution humans have developed a cognitive system that can detect even small distortions, which makes them feel uncomfortable when they detect some distortions in certain objects.
Recently, areas that involve in uncanny valley in the human brain were found. In 2019, a joint research team from the Department of Physiology at Cambridge University and the Human Technology Center at RWTH Aachen University found that the prefrontal cortex in the brain involve in uncanny valley. The research team conducted an experiment that showed participants an actual person, a mannequin, an Android robot, and an industrial robot and made them evaluate human likeness and likeability of the objects. The research team then observed which areas in the brain were activated through functional magnetic resonance imaging, fMRI. They identified that two areas in medial prefrontal cortex were activated. The medial prefrontal cortex judges external stimuli, one of which determines whether the stimuli are human faces. This area was more activated as the object that the participants viewed resembled a human being. The other is an area which feels likeability toward the stimuli. This area became more activated as the objects resembled humans, but for objects with higher similarity like Android robots, the degree of activation decreased.
Is it a Generational Phenomenon?
Uncanny valley phenomenon is considered a major psychological factor to the extent that affects box office hits. Many roboticist and graphic designers, therefore, are striving to overcome uncanny valley. But on the other side, some people point out the limits of uncanny valley theory. David Hanson, a founder of Hanson Robotics, claimed that uncanny valley is a generational phenomenon that will naturally disappear as new generations become accustomed to robots. It means that we feel unpleasant because such robots or graphics are not yet familiar to our generation. In fact, in the 1970s, when uncanny valley theory was created, it was difficult for people to experience such unpleasant feelings because the era was before semi-realistic robots and technology were developed. In other words, uncanny valley phenomenon can be viewed as a matter of ‘adaptation.’
With the development of various technologies, including artificial intelligence and robots, people see new objects that they have never seen before. Among the objects, some unfamiliar non-human beings may make us feel unpleasant. Somewhere in between human beings and non-human beings. Our rejection to them may be an instinctive psychological artifact to protect the existence of human beings. Although there is a limit to whether the theory can be generalized to transcend time, it seems certain that the theory was an innovative discovery about human psychology. In order not to fall into the valley, many scientists and engineers continue to study the aesthetic elements of ‘how should it look.’


